Function of HIV Reverse transcriptase (RT)
RT is another important enzyme encoded by the pol gene [1].
To produce dsDNA from the viral single-stranded RNA genome, RT in the reverse transcriptase complex (RTC) catalyzes both the RNA-dependent and the DNA-dependent DNA polymerization reactions.
During reverse transcription, RT jumps from one template to another when two copies of single-stranded genomic RNAs exist per virion. The frequent template switch promotes the generation of novel recombinant DNA genome sequences derived from two parental RNA sequences [1].
Reference
Xue B, Mizianty MJ, Kurgan L, Uversky VN: Protein intrinsic disorder as a flexible armor and a weapon of HIV-1. Cell Mol Life Sci 2012, 69:1211-1259.(Download Article)
Sequence
(1) Reference sequence for HIV-1 Reverse transcriptase
1 10 20 30 40 50
| | | | | |
PISPIETVPV KLKPGMDGPK VKQWPLTEEK IKALVEICTE MEKEGKISKI
51 60 70 80 90 100
| | | | | |
GPENPYNTPV FAIKKKDSTK WRKLVDFREL NKRTQDFWEV QLGIPHPAGL
101 110 120 130 140 150
| | | | | |
KKKKSVTVLD VGDAYFSVPL DEDFRKYTAF TIPSINNETP GIRYQYNVLP
151 160 170 180 190 200
| | | | | |
QGWKGSPAIF QSSMTKILEP FRKQNPDIVI YQYMDDLYVG SDLEIGQHRT
201 210 220 230 240 250
| | | | | |
KIEELRQHLL RWGLTTPDKK HQKEPPFLWM GYELHPDKWT VQPIVLPEKD
251 260 270 280 290 300
| | | | | |
SWTVNDIQKL VGKLNWASQI YPGIKVRQLC KLLRGTKALT EVIPLTEEAE
301 310 320 330 340 350
| | | | | |
LELAENREIL KEPVHGVYYD PSKDLIAEIQ KQGQGQWTYQ IYQEPFKNLK
351 360 370 380 390 400
| | | | | |
TGKYARMRGA HTNDVKQLTE AVQKITTESI VIWGKTPKFK LPIQKETWET
401 410 420 430 440 450
| | | | | |
WWTEYWQATW IPEWEFVNTP PLVKLWYQLE KEPIVGAETF YVDGAANRET
451 460 470 480 490 500
| | | | | |
KLGKAGYVTN RGRQKVVTLT DTTNQKTELQ AIYLALQDSG LEVNIVTDSQ
501 510 520 530 540 550
| | | | | |
YALGIIQAQP DQSESELVNQ IIEQLIKKEK VYLAWVPAHK GIGGNEQVDK
551 560
| |
LVSAGIRKVL (2) Reference sequence for HIV-2 and SIV Reverse transcriptase
1 10 20 30 40 50
| | | | | |
PIAKVEPVKV ALKPGKDGPK LKQWPLSKEK IVALREICEK MEKDGQLEEA
51 60 70 80 90 100
| | | | | |
PPTNPYNTPT FAIKKKDKNK WRMLIDFREL NRVTQDFTEV QLGIPHPAGL
101 110 120 130 140 150
| | | | | |
AKRKRITVLD IGDAYFSIPL DEEFRQYTAF TLPSVNNAEP GKRYIYKVLP
151 160 170 180 190 200
| | | | | |
QGWKGSPAIF QYTMRHVLEP FRKANPDVTL VQYMDDILIA SDRTDLEHDR
201 210 220 230 240 250
| | | | | |
VVLQSKELLN SIGFSTPEEK FQKDPPFQWM GYELWPTKWK LQKIELPQRE
251 260 270 280 290 300
| | | | | |
TWTVNDIQKL VGVLNWAAQI YPGIKTKHLC RLIRGKMTLT EEVQWTEMAE
301 310 320 330 340 350
| | | | | |
AEYEENKIIL SQEQEGCYYQ EGKPLEATVI KSQDNQWSYK IHQEDKILKV
351 360 370 380 390 400
| | | | | |
GKFAKIKNTH TNGVRLLAHV IQKIGKEAIV IWGQVPKFHL PVEKDVWEQW
401 410 420 430 440 450
| | | | | |
WTDYWQVTWI PEWDFISTPP LVRLVFNLVK DPIEGEETYY TDGSCNKQSK
451 460 470 480 490 500
| | | | | |
EGKAGYITDR GKDKVKVLEQ TTNQQAELEA FLMALTDSGP KANIIVDSQY
501 510 520 530 540 550
| | | | | |
VMGIITGCPT ESESRLVNQI IEEMIKKSEI YVAWVPAHKG IGGNQEIDHL
551 559
| |
VSQGIRQVL (3) Coloring scheme for above amino acids
Amino acids with hydrophobic side chains (normally buried inside the protein core):
A - Ala - Alanine
I - Ile - Isoleucine
L - Leu - Leucine
M - Met - Methionine
V - Val - Valine
Amino acids with polar uncharged side chains (may participate in hydrogen bonds):
N - Asn - Asparagine
Q - Gln - Glutamine
S - Ser - Serine
T - Thr - Threonine
Amino acids with positive charged side chains:
H - His - Histidine
K - Lys - Lysine
R - Arg - Arginine
Amino acids with negative charged side chains:
D - Asp - Aspartic acid
E - Glu - Glutamic acid
Amino acids with aromatic side chains:
F - Phe - Phenylalanine
Y - Tyr - Tyrosine
W - Trp - Tryptophan
Cysteine: C - Cys - Cysteine
Glycine: G - Gly - Glycine
Proline: P - Pro - Proline
Amino acid variations at HIV-1 Reverse transcriptase
Here, we visualize the prevalence of amino acid variations at the HIV-1 Reverse transcriptase from HIV-1 subtype B.
Protocal of our sequence collection
For HIV-1 subtype B, one sequence per patient was extracted from HIV Los Alamos database (www.hiv.lanl.gov/).
We removed misclassified sequences or sequences with hypermutations, stop codons, ambiguous nucleotides, which were described in our article [1].
We removed sequences conferred partial or full resistance to any of the Reverse transcriptase inhibitors, RT inhibitors and integrase inhibitors using HIVdb V6.0 .
Visualization
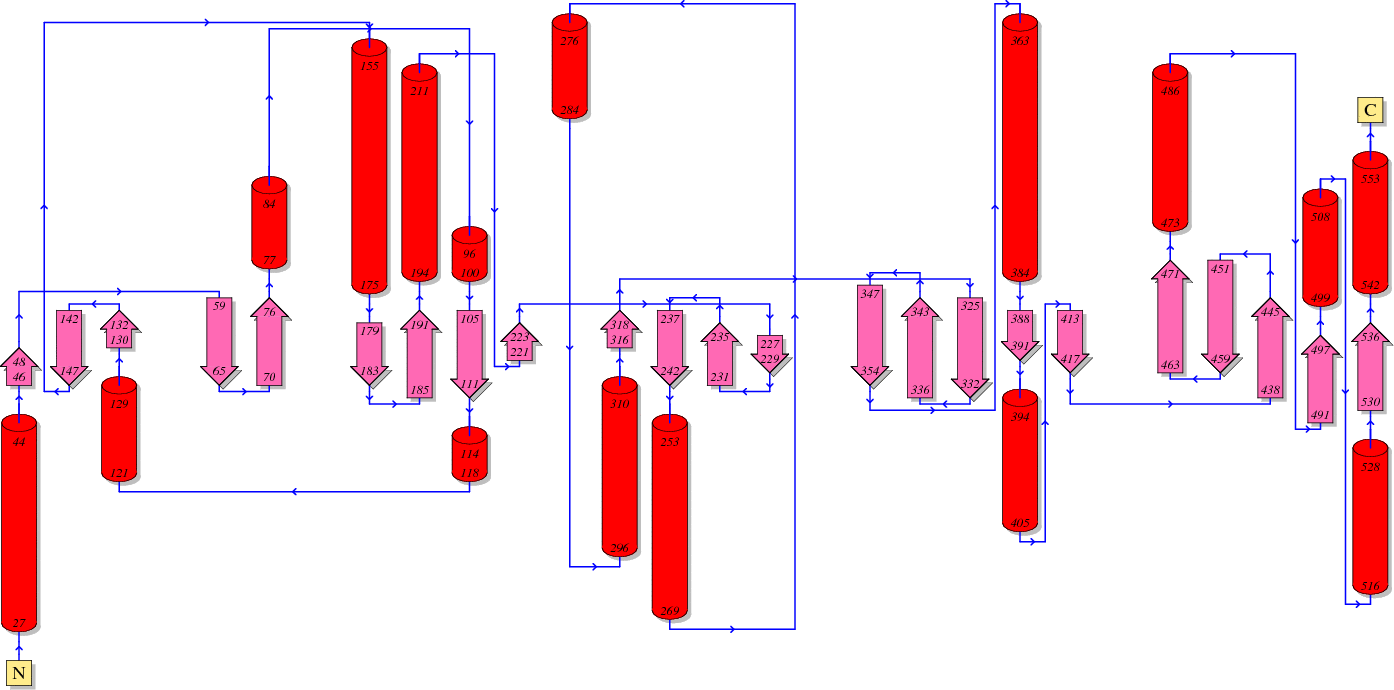
Our sequence dataset of HIV-1 subtype B Reverse transcriptase included 4725 sequences. In the following picture, HXB2 indices of individual proteins are shown on top of the colored bars. A consensus amino acid at each position is shown beneath the colored bar. Natural variations are shown below the consensus amino acids; proportions (%) are colored red if they were more than 5%; blue otherwise.
HIV-1 protein interaction patterns.
Please cite our article:
Guangdi Li, Supinya Piampongsant, Nuno Rodrigues Faria, Arnout Voet, Andrea-Clemencia Pineda-Peña, Ricardo Khouri, Philippe Lemey, Anne-Mieke Vandamme, Kristof Theys. An integrated map of HIV genome-wide variation from a population perspective. Retrovirology 12, 18, doi:10.1186/s12977-015-0148-6 (2015). [PDF] [PubMed Link]