Function of HIV Gag
- HIV Gag is a structural protein encoded by the gag gene, which provides the basic infrastructure of HIV particles [1].
- Gag in the plasma membrane can recruit host factors (e.g. TIP47) into nascent HIV particles [2].
- Many inhibitors have been developed to target drug binding sites in HIV-1 Gag [3].
Reference
- Bell, N. M. & Lever, A. M. HIV Gag polyprotein: processing and early viral particle assembly. Trends in microbiology 21, 136-144, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2012.11.006 (2013). [PubMed Link]
- Waheed, A. A. & Freed, E. O. HIV type 1 Gag as a target for antiviral therapy. AIDS research and human retroviruses 28, 54-75, doi:10.1089/AID.2011.0230 (2012). [PubMed Link]
- Guangdi Li, Jens Verheyen, Soo-Yon Rhee, Arnout Voet, Anne-Mieke Vandamme, Kristof Theys. Functional conservation of HIV-1 Gag: implications for rational drug design. Retrovirology. 10:126. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-126 (2013). [PubMed Link]
Sequence
(1) Reference sequence for HIV-1 Gag
1 10 20 30 40 50
| | | | | |
MGARASVLSG GELDRWEKIR LRPGGKKKYK LKHIVWASRE LERFAVNPGL
51 60 70 80 90 100
| | | | | |
LETSEGCRQI LGQLQPSLQT GSEELRSLYN TVATLYCVHQ RIEIKDTKEA
101 110 120 130 140 150
| | | | | |
LDKIEEEQNK SKKKAQQAAA DTGHSNQVSQ NYPIVQNIQG QMVHQAISPR
151 160 170 180 190 200
| | | | | |
TLNAWVKVVE EKAFSPEVIP MFSALSEGAT PQDLNTMLNT VGGHQAAMQM
201 210 220 230 240 250
| | | | | |
LKETINEEAA EWDRVHPVHA GPIAPGQMRE PRGSDIAGTT STLQEQIGWM
251 260 270 280 290 300
| | | | | |
TNNPPIPVGE IYKRWIILGL NKIVRMYSPT SILDIRQGPK EPFRDYVDRF
301 310 320 330 340 350
| | | | | |
YKTLRAEQAS QEVKNWMTET LLVQNANPDC KTILKALGPA ATLEEMMTAC
351 360 370 380 390 400
| | | | | |
QGVGGPGHKA RVLAEAMSQV TNSATIMMQR GNFRNQRKIV KCFNCGKEGH
401 410 420 430 440 450
| | | | | |
TARNCRAPRK KGCWKCGKEG HQMKDCTERQ ANFLGKIWPS YKGRPGNFLQ
451 460 470 480 490 500
| | | | | |
SRPEPTAPPE ESFRSGVETT TPPQKQEPID KELYPLTSLR SLFGNDPSSQ (2) Reference sequence for HIV-2 and SIV Gag
1 10 20 30 40 50
| | | | | |
MGVRNSVLSG KKADELEKIR LRPNGKKKYM LKHVVWAANE LDRFGLAESL
51 60 70 80 90 100
| | | | | |
LENKEGCQKI LSVLAPLVPT GSENLKSLYN TVCVIWCIHA EEKVKHTEEA
101 110 120 130 140 150
| | | | | |
KQIVQRHLVV ETGTTETMPK TSRPTAPSSG RGGNYPVQQI GGNYVHLPLS
151 160 170 180 190 200
| | | | | |
PRTLNAWVKL IEEKKFGAEV VPGFQALSEG CTPYDINQML NCVGDHQAAM
201 210 220 230 240 250
| | | | | |
QIIRDIINEE AADWDLQHPQ PAPQQGQLRE PSGSDIAGTT SSVDEQIQWM
251 260 270 280 290 300
| | | | | |
YRQQNPIPVG NIYRRWIQLG LQKCVRMYNP TNILDVKQGP KEPFQSYVDR
301 310 320 330 340 350
| | | | | |
FYKSLRAEQT DAAVKNWMTQ TLLIQNANPD CKLVLKGLGV NPTLEEMLTA
351 360 370 380 390 400
| | | | | |
CQGVGGPGQK ARLMAEALKE ALAPVPIPFA AAQQRGPRKP IKCWNCGKEG
401 410 420 430 440 450
| | | | | |
HSARQCRAPR RQGCWKCGKM DHVMAKCPDR QAGFLGLGPW GKKPRNFPMA
451 460 470 480 490 500
| | | | | |
QVHQGLMPTA PPEDPAVDLL KNYMQLGKQQ REKQRESREK PYKEVTEDLL
501 510
| |
HLNSLFGGDQ (3) Coloring scheme for above amino acids
Amino acids with hydrophobic side chains (normally buried inside the protein core):
A - Ala - Alanine
I - Ile - Isoleucine
L - Leu - Leucine
M - Met - Methionine
V - Val - Valine
Amino acids with polar uncharged side chains (may participate in hydrogen bonds):
N - Asn - Asparagine
Q - Gln - Glutamine
S - Ser - Serine
T - Thr - Threonine
Amino acids with positive charged side chains:
H - His - Histidine
K - Lys - Lysine
R - Arg - Arginine
Amino acids with negative charged side chains:
D - Asp - Aspartic acid
E - Glu - Glutamic acid
Amino acids with aromatic side chains:
F - Phe - Phenylalanine
Y - Tyr - Tyrosine
W - Trp - Tryptophan
Cysteine: C - Cys - Cysteine
Glycine: G - Gly - Glycine
Proline: P - Pro - Proline
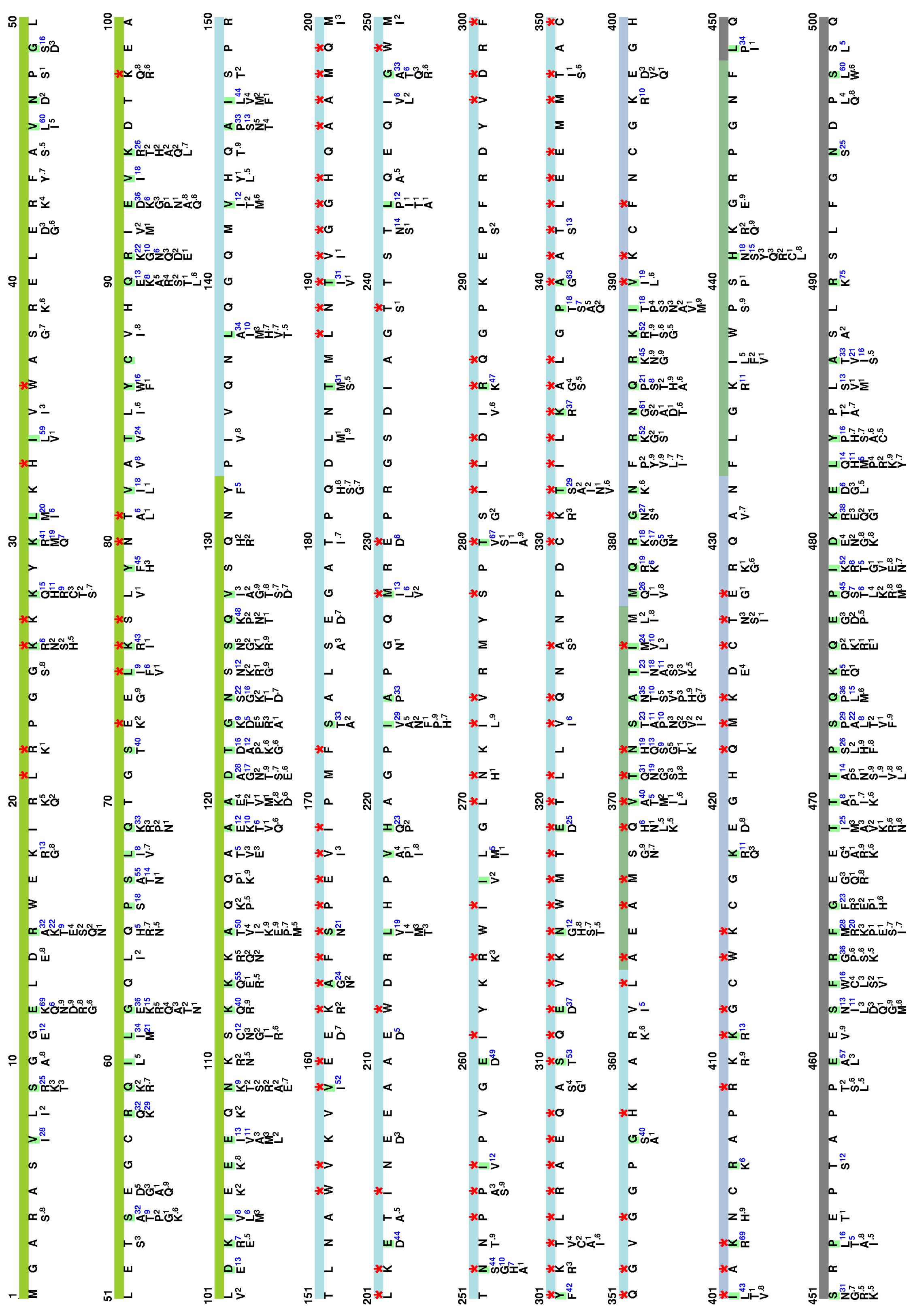
Amino acid variations at HIV-1 Gag
Here, we visualize the prevalence of amino acid variations at the HIV-1 Gag from HIV-1 group M.
Protocal of our sequence collection
Detailed protocals have been described in our publication:
Guangdi Li, Jens Verheyen, Soo-Yon Rhee, Arnout Voet, Anne-Mieke Vandamme, Kristof Theys. Functional conservation of HIV-1 Gag: implications for rational drug design. Retrovirology. 10:126. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-126 (2013). [PubMed Link]
Visualization of natural polymorphisms in Gag
Please cite our article:
Guangdi Li, Jens Verheyen, Soo-Yon Rhee, Arnout Voet, Anne-Mieke Vandamme, Kristof Theys. Functional conservation of HIV-1 Gag: implications for rational drug design. Retrovirology. 10:126. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-126 (2013). [PubMed Link]